Symptoms
Vein Symptom Guide
Please click one of the tabs below
Varicose veins are enlarged, ropy veins that bulge like cords beneath the surface of the skin, frequently dark blue or purple in color. Although varicose veins can occur anywhere on the body, they are most likely to appear on the legs. Varicose veins are very common, with around 80 million Americans affected by them.
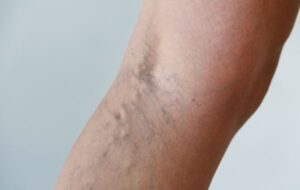
Varicose veins are superficial veins that have become abnormally dilated due to improper blood flow. When working properly, veins have valves that prevent blood from flowing backward. When these valves fail, blood pools and pressure builds with the veins, causing the veins to dilate and become more visible, as well as uncomfortable. Varicose veins can cause aching, itching, and throbbing, as well as burning and cramping.
What Causes Varicose Veins?
Risk factors for developing varicose veins including having a family history of venous disorders, obesity, pregnancy, aging, gender (women are more likely to develop varicose veins), and working in an environment that requires you to stand on your feet or sit for long periods of time.
What Treatments are Available for Varicose Veins?
Exercise, elevating your legs and wearing compression stockings to promote proper blood flow and reduce swelling can improve comfort levels. However, to prevent varicose veins from becoming worse and to improve comfort and appearance, patients will need to see a vein specialist for treatment.
Thanks to cutting-edge advancements in vein care, a vein specialist can achieve excellent results in eliminating varicose veins with minimally-invasive procedures. Your doctor will perform an ultrasound to identify problem veins and determine the best course of treatment. At The Vein Institute, Dr. Gardner may recommend one or a combination of the following therapies
- Sclerotherapy
- Endovenous laser ablation techniques
- Radiofrequency ablation techniques
- Microphlebectomy
Depending on the stage of venous disease, patients may experience a significant level of leg pain or discomfort. This pain happens for several different reasons. First, there are pain fibers in the walls of veins that sense when a vein is stretched. As the blood pools in the legs, pressure is generated and the veins become stretched causing pain. Secondly, as blood pools in the legs pressure pushes blood plasma into the soft tissues causing swelling of the lower legs. This puts undue pressure on the skin that causes pain.
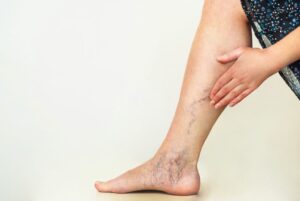
Other symptoms of chronic venous disease include a feeling of heaviness in the legs, cramps, swelling, skin tightness and/or thickening, itching, and the formation of ulcers around the ankles. Sensations of pain may increase when the patient has been standing and may improve when the legs are elevated.
At The Vein Institute, Dr. Gardner may recommend one of the following (or a combination of procedures) to eliminate diseased veins and restore comfort and mobility:
- Sclerotherapy
- Endovenous Laser Ablation (EVLA)
- Radiofrequency Laser Ablation (RF)
- Microphlebectomy
Swollen legs are a very common symptom seen in patients with venous disease. Malfunctioning valves within the veins allow blood to pool, increasing the pressure within the veins. This creates a condition known as “edema,” in which fluid seeps out into the surrounding soft tissues and accumulates there, resulting in swelling and tightening of the skin. Edema can be very uncomfortable. Other causes of leg swelling include blood clots, heart problems, kidney dysfunction, hormonal imbalances, and liver damage.
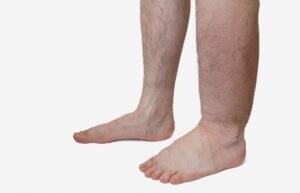
How Do You Treat Leg Swelling Due to Venous Disease?
In order to treat a patient’s leg swelling, a doctor must first determine the cause. The underlying condition must be treated to relieve any symptoms, and what works for swelling caused by venous insufficiency will not necessarily work for swelling caused by other conditions. A color duplex ultrasound exam will allow the doctor to identify whether the edema is caused by venous disease so that he can determine the most efficacious treatment.
If venous insufficiency is indeed causing the edema, Dr. Gardner may recommend compression stockings for short-term relief, and endovenous laser ablation techniques to eliminate the affected veins.
Many patients do not immediately connect leg ulcerations with a vein disorder—instead thinking it is strictly a problem of the skin. However, these painful, open sores, often located on or above the ankles, are a sign that blood in the veins is not being circulated back to the heart properly. As blood backs up in the veins this causes fluid to build up in the skin and soft tissues. This leads to increased pressure that causes breaks in the skin and prevents oxygen from getting to the tissues. Cell death occurs, ultimately damaging the skin and allowing sores to form and grow. These wounds can become infected if not dealt with properly and can be very slow to heal.
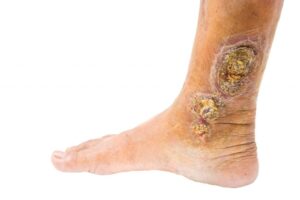
How are Venous Skin Ulcers Treated?
Your doctor will determine which veins are causing the ulcerations with an ultrasound exam. Once the problem veins have been identified, your doctor will come up with a personalized treatment plan using modern treatment methods to eliminate the diseased veins. This may include endovenous laser ablation techniques and/or ultrasound-guided sclerotherapy techniques. The ulcers may take a month or two to heal, depending on the size and depth of the wounds. Your doctor may advise you to wear compression stockings to promote healing until the wounds are completely healed.
An outcome of long-term, advanced chronic vein disease which many do not anticipate is change to skin pigmentation. Patients tend to expect the fatigue, discomfort, and the appearance of spider or varicose veins. In can be an unpleasant surprise that long-standing venous disorders may lead to a darkened appearance over the affected areas.
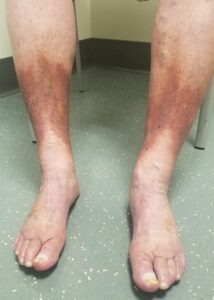
Typical changes in skin pigmentation present a reddish-brown stain that usually appears over the lower legs, starting at the ankle and moving up the leg. The pigmentation darkens over time—it may appear faint at first but will eventually become more pronounced as the condition worsens. With the veins malfunctioning beneath the skin, the pressure within the veins builds, forcing red blood cells to seep out and into the surrounding soft tissues. The red cells then burst, releasing hemoglobin. The iron in the hemoglobin stains the skin. Not only is the pigmentation unsightly, but it can also cause extreme itching. Many patients find the itching to be more disturbing than the color change.
How Do You Treat Skin Pigment Changes?
Successful treatment of the underlying vein disease should halt worsening of the pigment changes. Over time the pigment changes will fade, much like a tattoo.
Foot, leg, and ankle swelling is also known as edema, which refers to an accumulation of fluid in this part of the body. The most common cause of ankle swelling is due to some degree of venous (circulation) or lymphatic damage.
How we diagnose:
- Initial Consultation
- Assessment
- Ultrasound
- Treatment Plan
How we treat?
- Radiofrequency Ablation (Venclose)
- Sclerotherapy
- Non thermal Ablation (Venaseal)
- Micro-foam Sclerotherapy (Varithena)
Leg heaviness, or a sensation of aching fatigue in the legs, can be due to multiple cause including muscular disorders, joint issues, and circulatory disorders. A very common cause is venous insufficiency, or vein disease.
How we diagnose:
- Initial Consultation
- Assessment
- Ultrasound
- Treatment Plan
How we treat:
- Radiofrequency Ablation (VenClose)
- Compounded Sclerotherapy
- Non thermal Ablation (Venaseal)
- Micro-foam Sclerotherapy (Varithena)
Cramping is often thought to be caused by deficiency of potassium or dehydration, while true this is not the most common cause. Most people who have reoccurring day or night leg cramps have a circulation problem.
How we diagnose:
- Initial Consultation
- Assessment
- Ultrasound
- Treatment Plan
How we treat:
- Radiofrequency Ablation (VenClose)
- Sclerotherapy
- Non thermal Ablation (Venaseal)
- Micro-foam Sclerotherapy (Varithena)
Restless leg, an uncontrollable urge to move your leg, is very often caused by leg circulation problems. Medication is often prescribed which tends to mask the actual problem.
How we diagnose:
- Initial Consultation
- Assessment
- Ultrasound
- Treatment Plan
How we treat:
- Radiofrequency Ablation (Venclose)
- Sclerotherapy
- Non thermal Ablation (Venaseal)
- Micro-foam Sclerotherapy (Varithena)
Leg burning or itching is often due to poor blood flow to the skin and oil glands. This is a very common symptom of a circulation problem.
How we diagnose:
- Initial Consultation
- Assessment
- Ultrasound
- Treatment Plan
How we treat:
- Radiofrequency Ablation (Venclose)
- Sclerotherapy
- Non thermal Ablation (Venaseal)
- Micro-foam Sclerotherapy (Varithena)
Lipodermatosclerosis (LDS) is a condition commonly seen in patients who have chronic long-term venous disease. As with pigment changes and stasis dermatitis, lipodermatosclerosis occurs when blood pools within the veins, leading to increased pressure and leakage of fluid beneath the surface of the skin. This results in ongoing inflammation in the subcutaneous fat and surrounding tissues so that the skin begins to feel thickened and tough or “woody.” Lipodermatosclerosis is a painful condition due to the swelling, pressure and chronic inflammation.
What Treatments Options are Available for Lipodermatosclerosis?
Unfortunately, once lipodermatosclerosis is established, it is difficult to reverse. The sooner a patient undergoes treatment to correct the underlying venous insufficiency, the better, as less permanent damage will have been done.
Treatment should be focused on improving comfort and function and preventing the lipodermatosclerosis from progressing into ulcers. Patients may find temporary improvement of symptoms with compression stockings, but further treatment is necessary to keep the condition from progressing. Treatments for lipodermatosclerosis include:
- Endovenous laser ablation techniques
- Ultrasound-guided sclerotherapy techniques
A common complaint from patients who suffer from chronic venous insufficiency is a red, itching rash. This rash, known as stasis dermatitis, is caused by the pooling of blood within the veins. Because the blood is not being moved properly through the veins, it builds up and causes increased pressure. The increased pressure leads to the leakage of a substance called fibrin, which is a fibrous protein necessary for the clotting of blood. When it seeps out into surrounding tissues instead of remaining within the veins, it causes inflammation and cell death, resulting in red, inflamed, and itching skin at the surface.
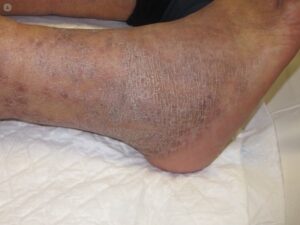
What Treatments are Available for Stasis Dermatitis?
Patients may get some relief from stasis dermatitis by wearing compression stockings that promote proper blood flow and reduce pooling. However, to get the best results, the underlying venous insufficiency must be resolved.
Spontaneous bleeding is an unpleasant and often unexpected occurrence for those who suffer from varicose veins. Bleeding can occur with or without an injury because the veins are so close to the surface and the skin is sometimes thin and easily broken. The veins most at risk of rupture are those around the ankle and feet, and this is most likely to occur after a shower.
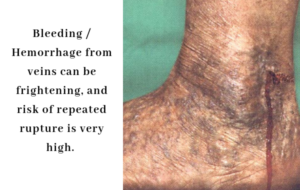
Bleeding is a troubling symptom for several reasons. The pressure within the veins is already quite high due to gravity and the failure of the valves that have led to vein disease in the first place. Due to this increased pressure, when the vein ruptures the blood may squirt out in a dramatic fashion, frightening the patient. While these bleeding veins are somewhat uncommon and unlikely to be life-threatening, bleeding should always be taken seriously and treated promptly.
What Treatments are Available?
Once the veins with high venous pressure are identified, Dr. Gardner will recommend a personalized treatment plan to address the problem veins. He may recommend several different treatment options, including endovenous laser ablation, microphlebectomy, and sclerotherapy. Bleeding should not recur in a vein that has been properly treated with modern treatment methods.
Most DVTs are completely asymptomatic. And although symptoms may not always be present with a DVT, there are some common signs to be aware of. You should seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Swelling of the leg
- Pain, which may or may not be severe, or tenderness in the leg, which may increase when you put weight on the limb or walk
- Leg feels warmer to the touch in the swollen area than in the surrounding tissue
- Skin is discolored – typically red or purplish in tone
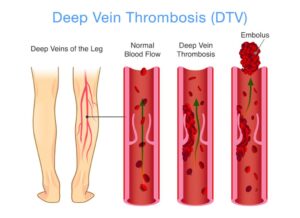
What Treatment Options are Available for Deep Vein Thrombosis or DVT?
Once you have been diagnosed with DVT, you will be placed on an anticoagulant, or blood thinner. This is initially done with an injectable blood thinner such as enoxaparin (Lovenox) and then converted to a longer lasting blood thinner such as warfarin (Coumadin). There are numerous newer blood thinners such as dabigatran (Pradaxa), rivaroxaban (Xarelto), apixaban (Eliquis), and edoxaban (Savaysa). These medicines prevent the blood from clotting further so that the clot does not continue to grow. In some cases, a catheter may be used to deliver special drugs directly to the affected vein to dissolve the clot. Your doctor will monitor your case closely to ensure your health and safety.
When a patient suffers from thrombophlebitis, their leg may become swollen, firm to the touch, discolored and tender. If the vein is not unblocked so that blood can circulate freely, tissue death may occur, followed by infection.
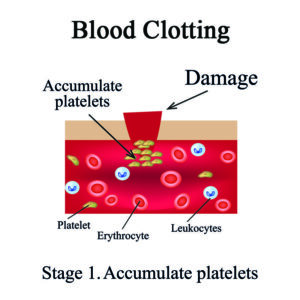
What are the Treatment Options for Thrombophlebitis?
If your doctor suspects that you have developed thrombophlebitis, he will perform a duplex ultrasound to identify the problem and locate the area of concern. Depending on the size and location of the clot, and your general medical condition, he may recommend a variety of treatment options including over the counter non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDS), compression stockings and leg elevation for symptom relief.
Some patients may also be given blood thinners, but this is more common for clots that form in the deep veins. In some cases, microphlebectomy may be utilized to treat the underlying cause. Your doctor will make a personalized recommendation based on your unique needs to provide you with the safest and best results.
Lymphedema is a swelling caused by a collection of lymph fluid, typically in the arms and legs, though it can also occur in other parts of the body. The swelling is so minor you don’t even notice it, or so severe it hinders movement of that part of the body.
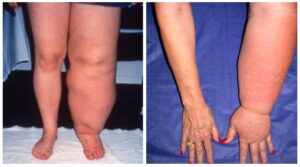
The lymphatic system is part of your body’s immune system. Lymph is a protein-rich fluid that moves throughout the body in lymph vessels, transporting bacteria, viruses, and waste to our lymph nodes, where they are then filtered out of the body.
What are the Symptoms of Lymphedema?
The primary symptom of lymphedema is swelling in one or both arms or legs, which may extend to the fingers or toes. This typically develops over time, first soft and fluid, becoming more dense and fibrous. It can also cause the texture of the skin to appear grainy.
Other symptoms include:
- Pain
- Heaviness
- Limited range of motion in the affected limb
What are the Treatment Options for Lymphedema?
Diagnosis is typically done with ultrasound tests. Lymphedema cannot be cured, but it can be treated and managed. Treatment options could include compression therapy, exercise, bandage wrappings, or massage. If it is severe, your doctor may want to do surgery to remove some tissue so there’s less swelling.
Phlebolymphedema is a swelling that occurs when the lymphatic system is unable to adequately drain lymph fluid that has accumulated in severe chronic venous hypertension. The circulatory and lymphatic systems maintain a delicate balance in the body. If the venous system is damaged, it will typically affect the lymphatic vessel system.
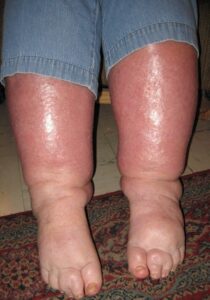
What are the Symptoms of Phlebolymphedema?
Often, symptoms do not occur until several years after injury to the lymphatic system. It is not unusual for patients with phlebolymphedema to experience swelling in the evening. Other symptoms include:
- Swelling of part or the entire limb, including toes or fingers
- Heaviness or tightness
- Weakness
- Diminished joint flexibility
- Aching or discomfort
- Recurring infections
- Hardening, thickening, or discoloration of the overlying skin
What are the Treatment Options for Phlebolymphedema?
There is no cure for this condition, but there are treatments that will help you to manage it, minimizing discomfort and reducing the swelling. Often treatment will include compression therapy, massage, and light exercise. Vein treatments are also used in some cases to relieve the pressure by removing excess fluid.
Varicose Veins
Varicose veins are enlarged, ropy veins that bulge like cords beneath the surface of the skin, frequently dark blue or purple in color. Although varicose veins can occur anywhere on the body, they are most likely to appear on the legs. Varicose veins are very common, with around 80 million Americans affected by them.

Varicose veins are superficial veins that have become abnormally dilated due to improper blood flow. When working properly, veins have valves that prevent blood from flowing backward. When these valves fail, blood pools and pressure builds with the veins, causing the veins to dilate and become more visible, as well as uncomfortable. Varicose veins can cause aching, itching, and throbbing, as well as burning and cramping.
What Causes Varicose Veins?
Risk factors for developing varicose veins including having a family history of venous disorders, obesity, pregnancy, aging, gender (women are more likely to develop varicose veins), and working in an environment that requires you to stand on your feet or sit for long periods of time.
What Treatments are Available for Varicose Veins?
Exercise, elevating your legs and wearing compression stockings to promote proper blood flow and reduce swelling can improve comfort levels. However, to prevent varicose veins from becoming worse and to improve comfort and appearance, patients will need to see a vein specialist for treatment.
Thanks to cutting-edge advancements in vein care, a vein specialist can achieve excellent results in eliminating varicose veins with minimally-invasive procedures. Your doctor will perform an ultrasound to identify problem veins and determine the best course of treatment. At The Vein Institute, Dr. Gardner may recommend one or a combination of the following therapies
- Sclerotherapy
- Endovenous laser ablation techniques
- Radiofrequency ablation techniques
- Microphlebectomy
Leg Pain
Depending on the stage of venous disease, patients may experience a significant level of leg pain or discomfort. This pain happens for several different reasons. First, there are pain fibers in the walls of veins that sense when a vein is stretched. As the blood pools in the legs, pressure is generated and the veins become stretched causing pain. Secondly, as blood pools in the legs pressure pushes blood plasma into the soft tissues causing swelling of the lower legs. This puts undue pressure on the skin that causes pain.

Other symptoms of chronic venous disease include a feeling of heaviness in the legs, cramps, swelling, skin tightness and/or thickening, itching, and the formation of ulcers around the ankles. Sensations of pain may increase when the patient has been standing and may improve when the legs are elevated.
At The Vein Institute, Dr. Gardner may recommend one of the following (or a combination of procedures) to eliminate diseased veins and restore comfort and mobility:
- Sclerotherapy
- Endovenous Laser Ablation (EVLA)
- Radiofrequency Laser Ablation (RF)
- Microphlebectomy
Leg Swelling
Swollen legs are a very common symptom seen in patients with venous disease. Malfunctioning valves within the veins allow blood to pool, increasing the pressure within the veins. This creates a condition known as “edema,” in which fluid seeps out into the surrounding soft tissues and accumulates there, resulting in swelling and tightening of the skin. Edema can be very uncomfortable. Other causes of leg swelling include blood clots, heart problems, kidney dysfunction, hormonal imbalances, and liver damage.

How Do You Treat Leg Swelling Due to Venous Disease?
In order to treat a patient’s leg swelling, a doctor must first determine the cause. The underlying condition must be treated to relieve any symptoms, and what works for swelling caused by venous insufficiency will not necessarily work for swelling caused by other conditions. A color duplex ultrasound exam will allow the doctor to identify whether the edema is caused by venous disease so that he can determine the most efficacious treatment.
If venous insufficiency is indeed causing the edema, Dr. Gardner may recommend compression stockings for short-term relief, and endovenous laser ablation techniques to eliminate the affected veins.
Venous Skin Ulcers / Leg Ulcers
Many patients do not immediately connect leg ulcerations with a vein disorder—instead thinking it is strictly a problem of the skin. However, these painful, open sores, often located on or above the ankles, are a sign that blood in the veins is not being circulated back to the heart properly. As blood backs up in the veins this causes fluid to build up in the skin and soft tissues. This leads to increased pressure that causes breaks in the skin and prevents oxygen from getting to the tissues. Cell death occurs, ultimately damaging the skin and allowing sores to form and grow. These wounds can become infected if not dealt with properly and can be very slow to heal.

How are Venous Skin Ulcers Treated?
Your doctor will determine which veins are causing the ulcerations with an ultrasound exam. Once the problem veins have been identified, your doctor will come up with a personalized treatment plan using modern treatment methods to eliminate the diseased veins. This may include endovenous laser ablation techniques and/or ultrasound-guided sclerotherapy techniques. The ulcers may take a month or two to heal, depending on the size and depth of the wounds. Your doctor may advise you to wear compression stockings to promote healing until the wounds are completely healed.
Pigment Skin Changes
An outcome of long-term, advanced chronic vein disease which many do not anticipate is change to skin pigmentation. Patients tend to expect the fatigue, discomfort, and the appearance of spider or varicose veins. In can be an unpleasant surprise that long-standing venous disorders may lead to a darkened appearance over the affected areas.

Typical changes in skin pigmentation present a reddish-brown stain that usually appears over the lower legs, starting at the ankle and moving up the leg. The pigmentation darkens over time—it may appear faint at first but will eventually become more pronounced as the condition worsens. With the veins malfunctioning beneath the skin, the pressure within the veins builds, forcing red blood cells to seep out and into the surrounding soft tissues. The red cells then burst, releasing hemoglobin. The iron in the hemoglobin stains the skin. Not only is the pigmentation unsightly, but it can also cause extreme itching. Many patients find the itching to be more disturbing than the color change.
How Do You Treat Skin Pigment Changes?
Successful treatment of the underlying vein disease should halt worsening of the pigment changes. Over time the pigment changes will fade, much like a tattoo.
Swelling of Foot, Leg, and/or Ankle
Foot, leg, and ankle swelling is also known as edema, which refers to an accumulation of fluid in this part of the body. The most common cause of ankle swelling is due to some degree of venous (circulation) or lymphatic damage.
How we diagnose:
- Initial Consultation
- Assessment
- Ultrasound
- Treatment Plan
How we treat?
- Radiofrequency Ablation (Venclose)
- Sclerotherapy
- Non thermal Ablation (Venaseal)
- Micro-foam Sclerotherapy (Varithena)
Leg Heaviness or Fatigue
Leg heaviness, or a sensation of aching fatigue in the legs, can be due to multiple cause including muscular disorders, joint issues, and circulatory disorders. A very common cause is venous insufficiency, or vein disease.
How we diagnose:
- Initial Consultation
- Assessment
- Ultrasound
- Treatment Plan
How we treat:
- Radiofrequency Ablation (VenClose)
- Compounded Sclerotherapy
- Non thermal Ablation (Venaseal)
- Micro-foam Sclerotherapy (Varithena)
Leg Cramps
Cramping is often thought to be caused by deficiency of potassium or dehydration, while true this is not the most common cause. Most people who have reoccurring day or night leg cramps have a circulation problem.
How we diagnose:
- Initial Consultation
- Assessment
- Ultrasound
- Treatment Plan
How we treat:
- Radiofrequency Ablation (VenClose)
- Sclerotherapy
- Non thermal Ablation (Venaseal)
- Micro-foam Sclerotherapy (Varithena)
Restless Legs
Restless leg, an uncontrollable urge to move your leg, is very often caused by leg circulation problems. Medication is often prescribed which tends to mask the actual problem.

How we diagnose:
- Initial Consultation
- Assessment
- Ultrasound
- Treatment Plan
How we treat:
- Radiofrequency Ablation (Venclose)
- Sclerotherapy
- Non thermal Ablation (Venaseal)
- Micro-foam Sclerotherapy (Varithena)
Burning or Itching Skin
Leg burning or itching is often due to poor blood flow to the skin and oil glands. This is a very common symptom of a circulation problem.
How we diagnose:
- Initial Consultation
- Assessment
- Ultrasound
- Treatment Plan
How we treat:
- Radiofrequency Ablation (Venclose)
- Sclerotherapy
- Non thermal Ablation (Venaseal)
- Micro-foam Sclerotherapy (Varithena)
Lipodermatosclerosis
Lipodermatosclerosis (LDS) is a condition commonly seen in patients who have chronic long-term venous disease. As with pigment changes and stasis dermatitis, lipodermatosclerosis occurs when blood pools within the veins, leading to increased pressure and leakage of fluid beneath the surface of the skin. This results in ongoing inflammation in the subcutaneous fat and surrounding tissues so that the skin begins to feel thickened and tough or “woody.” Lipodermatosclerosis is a painful condition due to the swelling, pressure and chronic inflammation.
What Treatments Options are Available for Lipodermatosclerosis?
Unfortunately, once lipodermatosclerosis is established, it is difficult to reverse. The sooner a patient undergoes treatment to correct the underlying venous insufficiency, the better, as less permanent damage will have been done.
Treatment should be focused on improving comfort and function and preventing the lipodermatosclerosis from progressing into ulcers. Patients may find temporary improvement of symptoms with compression stockings, but further treatment is necessary to keep the condition from progressing. Treatments for lipodermatosclerosis include:
- Endovenous laser ablation techniques
- Ultrasound-guided sclerotherapy techniques
Dermatitis
A common complaint from patients who suffer from chronic venous insufficiency is a red, itching rash. This rash, known as stasis dermatitis, is caused by the pooling of blood within the veins. Because the blood is not being moved properly through the veins, it builds up and causes increased pressure. The increased pressure leads to the leakage of a substance called fibrin, which is a fibrous protein necessary for the clotting of blood. When it seeps out into surrounding tissues instead of remaining within the veins, it causes inflammation and cell death, resulting in red, inflamed, and itching skin at the surface.

What Treatments are Available for Stasis Dermatitis?
Patients may get some relief from stasis dermatitis by wearing compression stockings that promote proper blood flow and reduce pooling. However, to get the best results, the underlying venous insufficiency must be resolved.
Spontaneous Bleeding/ Hemorrhage from Veins
Spontaneous bleeding is an unpleasant and often unexpected occurrence for those who suffer from varicose veins. Bleeding can occur with or without an injury because the veins are so close to the surface and the skin is sometimes thin and easily broken. The veins most at risk of rupture are those around the ankle and feet, and this is most likely to occur after a shower.

Bleeding is a troubling symptom for several reasons. The pressure within the veins is already quite high due to gravity and the failure of the valves that have led to vein disease in the first place. Due to this increased pressure, when the vein ruptures the blood may squirt out in a dramatic fashion, frightening the patient. While these bleeding veins are somewhat uncommon and unlikely to be life-threatening, bleeding should always be taken seriously and treated promptly.
What Treatments are Available?
Once the veins with high venous pressure are identified, Dr. Gardner will recommend a personalized treatment plan to address the problem veins. He may recommend several different treatment options, including endovenous laser ablation, microphlebectomy, and sclerotherapy. Bleeding should not recur in a vein that has been properly treated with modern treatment methods.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Most DVTs are completely asymptomatic. And although symptoms may not always be present with a DVT, there are some common signs to be aware of. You should seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Swelling of the leg
- Pain, which may or may not be severe, or tenderness in the leg, which may increase when you put weight on the limb or walk
- Leg feels warmer to the touch in the swollen area than in the surrounding tissue
- Skin is discolored – typically red or purplish in tone

What Treatment Options are Available for Deep Vein Thrombosis or DVT?
Once you have been diagnosed with DVT, you will be placed on an anticoagulant, or blood thinner. This is initially done with an injectable blood thinner such as enoxaparin (Lovenox) and then converted to a longer lasting blood thinner such as warfarin (Coumadin). There are numerous newer blood thinners such as dabigatran (Pradaxa), rivaroxaban (Xarelto), apixaban (Eliquis), and edoxaban (Savaysa). These medicines prevent the blood from clotting further so that the clot does not continue to grow. In some cases, a catheter may be used to deliver special drugs directly to the affected vein to dissolve the clot. Your doctor will monitor your case closely to ensure your health and safety.
Thrombophlebitis
When a patient suffers from thrombophlebitis, their leg may become swollen, firm to the touch, discolored and tender. If the vein is not unblocked so that blood can circulate freely, tissue death may occur, followed by infection.

What are the Treatment Options for Thrombophlebitis?
If your doctor suspects that you have developed thrombophlebitis, he will perform a duplex ultrasound to identify the problem and locate the area of concern. Depending on the size and location of the clot, and your general medical condition, he may recommend a variety of treatment options including over the counter non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDS), compression stockings and leg elevation for symptom relief.
Some patients may also be given blood thinners, but this is more common for clots that form in the deep veins. In some cases, microphlebectomy may be utilized to treat the underlying cause. Your doctor will make a personalized recommendation based on your unique needs to provide you with the safest and best results.
Lymphedema
Lymphedema is a swelling caused by a collection of lymph fluid, typically in the arms and legs, though it can also occur in other parts of the body. The swelling is so minor you don’t even notice it, or so severe it hinders movement of that part of the body.

The lymphatic system is part of your body’s immune system. Lymph is a protein-rich fluid that moves throughout the body in lymph vessels, transporting bacteria, viruses, and waste to our lymph nodes, where they are then filtered out of the body.
What are the Symptoms of Lymphedema?
The primary symptom of lymphedema is swelling in one or both arms or legs, which may extend to the fingers or toes. This typically develops over time, first soft and fluid, becoming more dense and fibrous. It can also cause the texture of the skin to appear grainy.
Other symptoms include:
- Pain
- Heaviness
- Limited range of motion in the affected limb
What are the Treatment Options for Lymphedema?
Diagnosis is typically done with ultrasound tests. Lymphedema cannot be cured, but it can be treated and managed. Treatment options could include compression therapy, exercise, bandage wrappings, or massage. If it is severe, your doctor may want to do surgery to remove some tissue so there’s less swelling.
Phlebolymphedema
Phlebolymphedema is a swelling that occurs when the lymphatic system is unable to adequately drain lymph fluid that has accumulated in severe chronic venous hypertension. The circulatory and lymphatic systems maintain a delicate balance in the body. If the venous system is damaged, it will typically affect the lymphatic vessel system.

What are the Symptoms of Phlebolymphedema?
Often, symptoms do not occur until several years after injury to the lymphatic system. It is not unusual for patients with phlebolymphedema to experience swelling in the evening. Other symptoms include:
- Swelling of part or the entire limb, including toes or fingers
- Heaviness or tightness
- Weakness
- Diminished joint flexibility
- Aching or discomfort
- Recurring infections
- Hardening, thickening, or discoloration of the overlying skin
What are the Treatment Options for Phlebolymphedema?
There is no cure for this condition, but there are treatments that will help you to manage it, minimizing discomfort and reducing the swelling. Often treatment will include compression therapy, massage, and light exercise. Vein treatments are also used in some cases to relieve the pressure by removing excess fluid.
Vein Symptom Guide
Like varicose veins, spider veins are superficial dilated veins that are visible through the skin. However, spider veins are capillary veins, and as such, are much smaller and closer to the surface of the skin than varicose veins.
Spider veins (also known as telangiectasias) are known for their delicate, web-like appearance under the skin. They are usually red to blue in color, and may occur around the nose and mouth as well as the legs.

How do you Treat Spider Veins?
Spider veins are considered to be a cosmetic issue as they generally do not produce symptoms as varicose veins do. However, your doctor may recommend that you undergo a venous ultrasound when considering treatment for spider veins in the legs, to ensure there aren’t further issues within your veins.
If you have spider veins that you would like to have eliminated, your doctor may recommend sclerotherapy, in which a liquid or foam is injected into the problem veins to cause them to close and collapse, eventually disappearing. Your doctor may also choose to use a laser treatment to target the vein or a combination of laser and sclerotherapy treatments.
Varicose veins are enlarged, ropy veins that bulge like cords beneath the surface of the skin, frequently dark blue or purple in color. Although varicose veins can occur anywhere on the body, they are most likely to appear on the legs. Varicose veins are very common, with around 40 million Americans affected by them.

Varicose veins are superficial veins that have become abnormally dilated due to improper blood flow. When working properly, veins have valves that prevent blood from flowing backward. When these valves fail, blood pools and pressure builds with the veins, causing the veins to dilate and become more visible, as well as uncomfortable. Varicose veins can cause aching, itching, and throbbing, as well as burning and cramping.
What Causes Varicose Veins?
Risk factors for developing varicose veins including having a family history of venous disorders, obesity, pregnancy, aging, gender (women are more likely to develop varicose veins), and working in an environment that requires you to stand on your feet or sit for long periods of time.
What Treatments are Available for Varicose Veins?
Exercise, elevating your legs and wearing compression stockings to promote proper blood flow and reduce swelling can improve comfort levels. However, to prevent varicose veins from becoming worse and to improve comfort and appearance, patients will need to see a vein specialist for treatment.
Thanks to cutting-edge advancements in vein care, a vein specialist can achieve excellent results in eliminating varicose veins with minimally-invasive procedures. Your doctor will perform an ultrasound to identify problem veins and determine the best course of treatment. At The Vein Institute, Dr. Gardner may recommend one or a combination of the following therapies
- Sclerotherapy
- Endovenous laser ablation techniques
- Radiofrequency ablation techniques
- Microphlebectomy
Though not as well-known as varicose veins and spider veins, reticular veins may be just as visible and aesthetically undesirable. Reticular veins are larger than spider veins, generally blue in color, and visible from the surface though they are located more deeply under the skin. Reticular veins may exist on their own, or they may be connected to, and “feed,” spider veins.

Once a reticular vein has become diseased, the pressure builds, sometimes adding pressure to surrounding spider veins. The spider veins react to the increased pressure by bulging and becoming more visible.
What Treatments are Available for Reticular Veins?
Although reticular veins usually only cause mild discomfort, they should be treated to prevent progression of symptoms, especially if spider veins are also an issue. If only the spider veins are treated, the problem that created them will still exist. Your doctor may recommend any of the following treatments to achieve the most aesthetically pleasing results.
- Sclerotherapy
- Microphlebectomy
- Laser Treatments
- Or a combination of any of the above
Depending on the stage of venous disease, patients may experience a significant level of leg pain or discomfort. This pain happens for several different reasons. First, there are pain fibers in the walls of veins that sense when a vein is stretched. As the blood pools in the legs, pressure is generated and the veins become stretched causing pain. Secondly, as blood pools in the legs pressure pushes blood plasma into the soft tissues causing swelling of the lower legs. This puts undue pressure on the skin that causes pain.

Other symptoms of chronic venous disease include a feeling of heaviness in the legs, cramps, swelling, skin tightness and/or thickening, itching, and the formation of ulcers around the ankles. Sensations of pain may increase when the patient has been standing and may improve when the legs are elevated.
At The Vein Institute, Dr. Gardner may recommend one of the following (or a combination of procedures) to eliminate diseased veins and restore comfort and mobility:
- Sclerotherapy
- Endovenous Laser Ablation (EVLA)
- Radiofrequency Laser Ablation (RF)
- Microphlebectomy
Swollen legs are a very common symptom seen in patients with venous disease. Malfunctioning valves within the veins allow blood to pool, increasing the pressure within the veins. This creates a condition known as “edema,” in which fluid seeps out into the surrounding soft tissues and accumulates there, resulting in swelling and tightening of the skin. Edema can be very uncomfortable. Other causes of leg swelling include blood clots, heart problems, kidney dysfunction, hormonal imbalances, and liver damage.

How Do You Treat Leg Swelling Due to Venous Disease?
In order to treat a patient’s leg swelling, a doctor must first determine the cause. The underlying condition must be treated to relieve any symptoms, and what works for swelling caused by venous insufficiency will not necessarily work for swelling caused by other conditions. A color duplex ultrasound exam will allow the doctor to identify whether the edema is caused by venous disease so that he can determine the most efficacious treatment.
If venous insufficiency is indeed causing the edema, Dr. Gardner may recommend compression stockings for short-term relief, and endovenous laser ablation techniques to eliminate the affected veins.
Many patients do not immediately connect leg ulcerations with a vein disorder—instead thinking it is strictly a problem of the skin. However, these painful, open sores, often located on or above the ankles, are a sign that blood in the veins is not being circulated back to the heart properly. As blood backs up in the veins this causes fluid to build up in the skin and soft tissues. This leads to increased pressure that causes breaks in the skin and prevents oxygen from getting to the tissues. Cell death occurs, ultimately damaging the skin and allowing sores to form and grow. These wounds can become infected if not dealt with properly and can be very slow to heal.

How are Venous Skin Ulcers Treated?
Your doctor will determine which veins are causing the ulcerations with an ultrasound exam. Once the problem veins have been identified, your doctor will come up with a personalized treatment plan using modern treatment methods to eliminate the diseased veins. This may include endovenous laser ablation techniques and/or ultrasound-guided sclerotherapy techniques. The ulcers may take a month or two to heal, depending on the size and depth of the wounds. Your doctor may advise you to wear compression stockings to promote healing until the wounds are completely healed.
An outcome of long-term, advanced chronic vein disease which many do not anticipate is change to skin pigmentation. Patients tend to expect the fatigue, discomfort, and the appearance of spider or varicose veins. In can be an unpleasant surprise that long-standing venous disorders may lead to a darkened appearance over the affected areas.

Typical changes in skin pigmentation present a reddish-brown stain that usually appears over the lower legs, starting at the ankle and moving up the leg. The pigmentation darkens over time—it may appear faint at first but will eventually become more pronounces as the condition worsens. With the veins malfunctioning beneath the skin, the pressure within the veins builds, forcing red blood cells to seep out and into the surrounding soft tissues. The red cells then burst, releasing hemoglobin. The iron in the hemoglobin stains the skin. Not only is the pigmentation unsightly, but it can also cause extreme itching. Many patients find the itching to be more disturbing than the color change.
How Do You Treat Skin Pigment Changes?
Successful treatment of the underlying vein disease should halt worsening of the pigment changes. Over time the pigment changes will fade, much like a tattoo.
Foot, leg, and ankle swelling is also known as edema, which refers to an accumulation of fluid in this part of the body. The most common cause of ankle swelling is due to some degree of venous (circulation) or lymphatic damage.
How we diagnose:
- Initial Consultation
- Assessment
- Ultrasound
- Treatment Plan
How we treat?
- Radiofrequency Ablation (ClosureFast)
- Sclerotherapy
- Non thermal Ablation (Venaseal)
- Micro-foam Sclerotherapy (Varithena)
Leg heaviness, or a sensation of aching fatigue in the legs, can be due to multiple cause including muscular disorders, joint issues, and circulatory disorders. A very common cause is venous insufficiency, or vein disease.
How we diagnose:
- Initial Consultation
- Assessment
- Ultrasound
- Treatment Plan
How we treat:
- Radiofrequency Ablation (ClosureFast)
- Compounded Sclerotherapy
- Non thermal Ablation (Venaseal)
- Micro-foam Sclerotherapy (Varithena)
Cramping is often thought to be caused by deficiency of potassium or dehydration, while true this is not the most common cause. Most people who have reoccurring day or night leg cramps have a circulation problem.
How we diagnose:
- Initial Consultation
- Assessment
- Ultrasound
- Treatment Plan
How we treat:
- Radiofrequency Ablation (ClosureFast)
- Sclerotherapy
- Non thermal Ablation (Venaseal)
- Micro-foam Sclerotherapy (Varithena)
Restless leg, an uncontrollable urge to move your leg, is very often caused by leg circulation problems. Medication is often prescribed which tends to mask the actual problem.

How we diagnose:
- Initial Consultation
- Assessment
- Ultrasound
- Treatment Plan
How we treat:
- Radiofrequency Ablation (ClosureFast)
- Sclerotherapy
- Non thermal Ablation (Venaseal)
- Micro-foam Sclerotherapy (Varithena)
Leg burning or itching is often due to poor blood flow to the skin and oil glands. This is a very common symptom of a circulation problem.
How we diagnose:
- Initial Consultation
- Assessment
- Ultrasound
- Treatment Plan
How we treat:
- Radiofrequency Ablation (ClosureFast)
- Sclerotherapy
- Non thermal Ablation (Venaseal)
- Micro-foam Sclerotherapy (Varithena)
Lipodermatosclerosis (LDS) is a condition commonly seen in patients who have chronic long-term venous disease. As with pigment changes and stasis dermatitis, lipodermatosclerosis occurs when blood pools within the veins, leading to increased pressure and leakage of fluid beneath the surface of the skin. This results in ongoing inflammation in the subcutaneous fat and surrounding tissues so that the skin begins to feel thickened and tough or “woody.” Lipodermatosclerosis is a painful condition due to the swelling, pressure and chronic inflammation.
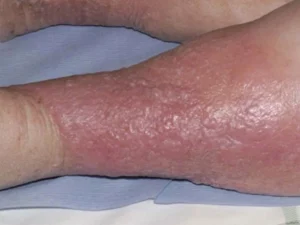
What Treatments Options are Available for Lipodermatosclerosis?
Unfortunately, once lipodermatosclerosis is established, it is difficult to reverse. The sooner a patient undergoes treatment to correct the underlying venous insufficiency, the better, as less permanent damage will have been done.
Treatment should be focused on improving comfort and function and preventing the lipodermatosclerosis from progressing into ulcers. Patients may find temporary improvement of symptoms with compression stockings, but further treatment is necessary to keep the condition from progressing. Treatments for lipodermatosclerosis include:
- Endovenous laser ablation techniques
- Ultrasound-guided sclerotherapy techniques
A common complaint from patients who suffer from chronic venous insufficiency is a red, itching rash. This rash, known as stasis dermatitis, is caused by the pooling of blood within the veins. Because the blood is not being moved properly through the veins, it builds up and causes increased pressure. The increased pressure leads to the leakage of a substance called fibrin, which is a fibrous protein necessary for the clotting of blood. When it seeps out into surrounding tissues instead of remaining within the veins, it causes inflammation and cell death, resulting in red, inflamed, and itching skin at the surface.

What Treatments are Available for Stasis Dermatitis?
Patients may get some relief from stasis dermatitis by wearing compression stockings that promote proper blood flow and reduce pooling. However, to get the best results, the underlying venous insufficiency must be resolved.
Spontaneous bleeding is an unpleasant and often unexpected occurrence for those who suffer from varicose veins. Bleeding can occur with or without an injury because the veins are so close to the surface and the skin is sometimes thin and easily broken. The veins most at risk of rupture are those around the ankle and feet, and this is most likely to occur after a shower.

Bleeding is a troubling symptom for several reasons. The pressure within the veins is already quite high due to gravity and the failure of the valves that have led to vein disease in the first place. Due to this increased pressure, when the vein ruptures the blood may squirt out in a dramatic fashion, frightening the patient. While these bleeding veins are somewhat uncommon and unlikely to be life-threatening, bleeding should always be taken seriously and treated promptly.
What Treatments are Available?
Once the veins with high venous pressure are identified, Dr. Gardner will recommend a personalized treatment plan to address the problem veins. He may recommend several different treatment options, including endovenous laser ablation, microphlebectomy, and sclerotherapy. Bleeding should not recur in a vein that has been properly treated with modern treatment methods.
Most DVTs are completely asymptomatic. And although symptoms may not always be present with a DVT, there are some common signs to be aware of. You should seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Swelling of the leg
- Pain, which may or may not be severe, or tenderness in the leg, which may increase when you put weight on the limb or walk
- Leg feels warmer to the touch in the swollen area than in the surrounding tissue
- Skin is discolored – typically red or purplish in tone

What Treatment Options are Available for Deep Vein Thrombosis or DVT?
Once you have been diagnosed with DVT, you will be placed on an anticoagulant, or blood thinner. This is initially done with an injectable blood thinner such as enoxaparin (Lovenox) and then converted to a longer lasting blood thinner such as warfarin (Coumadin). There are numerous newer blood thinners such as dabigatran (Pradaxa), rivaroxaban (Xarelto), apixaban (Eliquis), and edoxaban (Savaysa). These medicines prevent the blood from clotting further so that the clot does not continue to grow. In some cases, a catheter may be used to deliver special drugs directly to the affected vein to dissolve the clot. Your doctor will monitor your case closely to ensure your health and safety.
When a patient suffers from thrombophlebitis, their leg may become swollen, firm to the touch, discolored and tender. If the vein is not unblocked so that blood can circulate freely, tissue death may occur, followed by infection.

What are the Treatment Options for Thrombophlebitis?
If your doctor suspects that you have developed thrombophlebitis, he will perform a duplex ultrasound to identify the problem and locate the area of concern. Depending on the size and location of the clot, and your general medical condition, he may recommend a variety of treatment options including over the counter non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDS), compression stockings and leg elevation for symptom relief.
Some patients may also be given blood thinners, but this is more common for clots that form in the deep veins. In some cases, microphlebectomy may be utilized to treat the underlying cause. Your doctor will make a personalized recommendation based on your unique needs to provide you with the safest and best results.
Lymphedema is a swelling caused by a collection of lymph fluid, typically in the arms and legs, though it can also occur in other parts of the body. The swelling is so minor you don’t even notice it, or so severe it hinders movement of that part of the body.

The lymphatic system is part of your body’s immune system. Lymph is a protein-rich fluid that moves throughout the body in lymph vessels, transporting bacteria, viruses, and waste to our lymph nodes, where they are then filtered out of the body.
What are the Symptoms of Lymphedema?
The primary symptom of lymphedema is swelling in one or both arms or legs, which may extend to the fingers or toes. This typically develops over time, first soft and fluid, becoming more dense and fibrous. It can also cause the texture of the skin to appear grainy.
Other symptoms include:
- Pain
- Heaviness
- Limited range of motion in the affected limb
What are the Treatment Options for Lymphedema?
Diagnosis is typically done with ultrasound tests. Lymphedema cannot be cured, but it can be treated and managed. Treatment options could include compression therapy, exercise, bandage wrappings, or massage. If it is severe, your doctor may want to do surgery to remove some tissue so there’s less swelling.
Phlebolymphedema is a swelling that occurs when the lymphatic system is unable to adequately drain lymph fluid that has accumulated in severe chronic venous hypertension. The circulatory and lymphatic systems maintain a delicate balance in the body. If the venous system is damaged, it will typically affect the lymphatic vessel system.

What are the Symptoms of Phlebolymphedema?
Often, symptoms do not occur until several years after injury to the lymphatic system. It is not unusual for patients with phlebolymphedema to experience swelling in the evening. Other symptoms include:
- Swelling of part or the entire limb, including toes or fingers
- Heaviness or tightness
- Weakness
- Diminished joint flexibility
- Aching or discomfort
- Recurring infections
- Hardening, thickening, or discoloration of the overlying skin
What are the Treatment Options for Phlebolymphedema?
There is no cure for this condition, but there are treatments that will help you to manage it, minimizing discomfort and reducing the swelling. Often treatment will include compression therapy, massage, and light exercise. Surgical treatments are also used in extreme cases to relieve the pressure by removing excess tissue and fluid.

